mt-sDNA ALGORITHM1
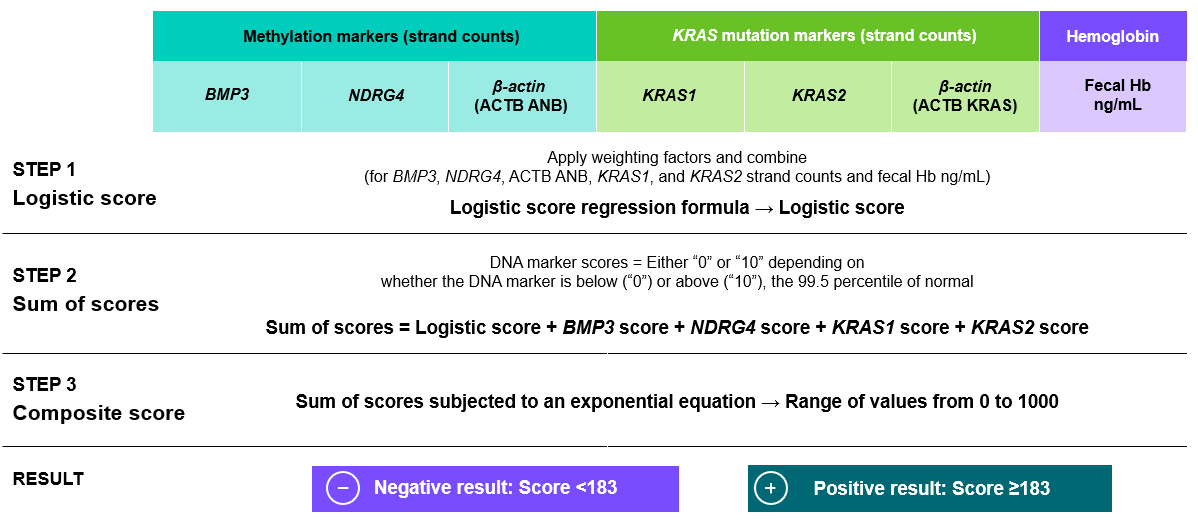
- Multiple genetic markers (strand counts) and hemoglobin are scored1
- A logistic score that applies weighting factors is added to other marker scores to determine the composite score1
- The mt-sDNA test is qualitative, only providing a dichotomous "positive" or “negative” result1
- A negative result is a composite score less than 183; a positive result is a composite score greater than or equal to 1831. The composite score is not linear, a higher score does not implicate a stronger positive result.
- The algorithm provides needed context to determine the test result and associated risk1
11 Distinct Biomarkers Produce a Qualitative Result1,2
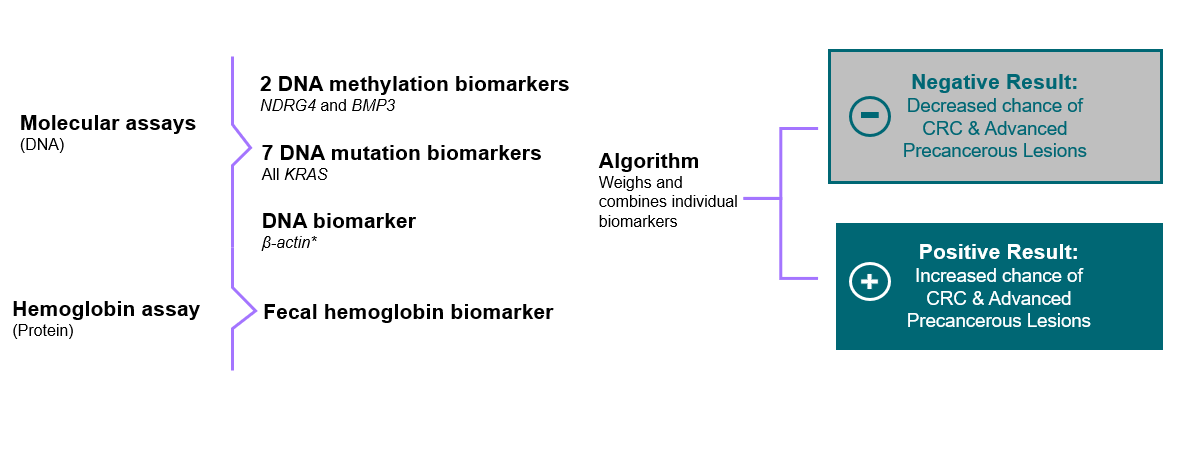
- Biomarkers do not have individually validated reference ranges, and each marker’s clinical significance is influenced by the other markers.1,2
- Therefore, biomarker levels cannot be interpreted separately, and the algorithm must incorporate all biomarker measurements to produce a result.1,2
- A positive result indicates that the biomarker combination has an increased association with CRC or advanced adenoma.1,2
- Any positive result should be followed by a colonoscopy.1,2
A Single Stool Sample Can Provide Evidence Of CRC And Precancerous Growths1,3
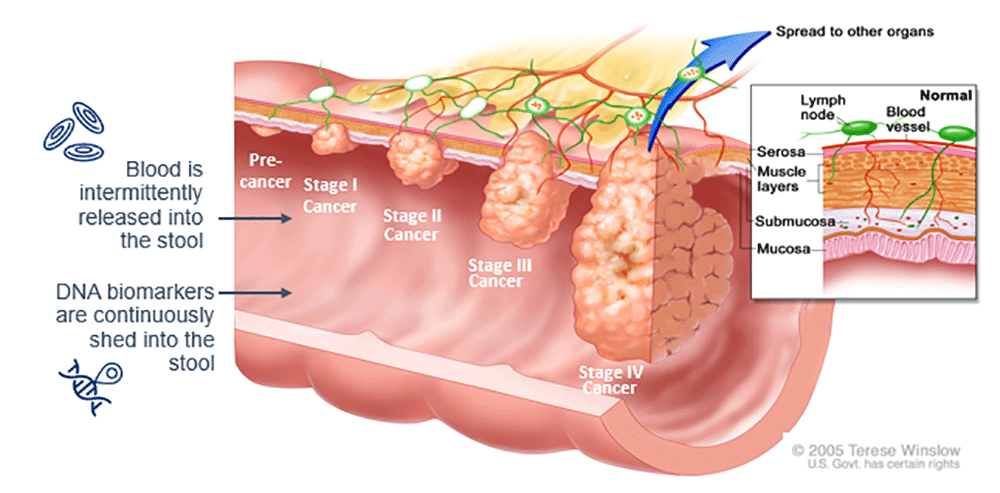
- As stool progresses through the colon and rectum, DNA sloughs from the lining of the colon and rectum as well as any blood that may be present1,3
- This DNA and blood serve as the biomarkers evaluated by the test1,3
- A single stool sample can present a snapshot of potential precancerous adenomas and colorectal carcinomas along the colon and rectum1,3
AA: advanced adenoma, ANB: gene panel of ACTB,
NDRG4, and BMP3, Hb: hemoglobin, BMP3: Bone Morphogenetic Protein 3, NDRG4: N-Myc Downstream-Regulated Gene 4, KRAS: v-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog, mt-sDNA: multi-target stool DNA
References
1 Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH, et al. Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(14):1287-1297.
2 Cologuard Clinician Brochure. Exact Sciences Corporation. Madison, WI.
3 Ahlquist DA. Multi-target stool DNA test: a new high bar for noninvasive screening. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60(3):623-633.
Footnotes
a The composite score is not linear, a higher score does not equal more risk above the 183 cutoff value.
bACTB is a reference gene for quantitative estimation of the total amount of human DNA in each sample.
Last updated: 04/17/2023